What is Mock testing?
In simple words, when we test a particular function, we use a different set of values (possible permutation of data) to make sure that the function works as expected. Then that can be called Mock testing.
What is a Unit function?
A unit function is the smallest possible thing that performs a particular task. Every business logic, even the addition of two numbers can be written as a Unit function.
What is Unit testing?
The function should be the smallest possible thing that performs a particular task, testing that function with the different possible scenarios is called Unit testing.
module.exports.checkIsAdult = (age) => {return age >= 18}
This can be called as a Unit function. All it does is one task (i.e)., Check whether the given value is greater than or equal to 18 or not
What is Mocking data?
- We change the data for testing the particular scenario in the production code.
- We have a list of scenarios that happen in production. So we need to test for all the possible scenarios. But we didn’t have all the data to test the production code. For that, we use a sample(base data) data. We modify those data for a particular scenario and use them to check the production code is working as expected or not.
Let’s write our first Unit test
Create a new project by initializing,
npm init -y
Create a new file called main.js in the project root directory. In that file we are exporting the checkIsAdult function,
module.exports.checkIsAdult = (age) => {return age >= 18}
Create a folder called test. And a file called sampledata.js in that test folder and export the sampleUserData data. Sample data of User
module.exports = {username: 'test user',email: 'abc@test.com',age: 30,password: 'password',userId: 324,}
Create a file Mockdata.js file in the test folder and import the sampleUserData. So that we can change it for different scenarios.
Mocked data for different scenario
const sampleUserData = require('./sampledata')//scenario #1 - User with age greater than 18module.exports.UserWithAgeGreaterThan18 = () => {const payload = { ...sampleUserData, age: 20 }return payload}//scenario #2 - User with age less than 18module.exports.UserWithAgeLessThan18 = () => {const payload = { ...sampleUserData, age: 17 }return payload}//scenario #3 - User with age equal to 18module.exports.UserWithAgeEqualTo18 = () => {const payload = { ...sampleUserData, age: 18 }return payload}
Here we returning the mocked data in a function. Because if we want to use them in a different place we can simply import them and call those function
Now, let’s test our checkIsAdult function. We are going to use Mocha and Chai for testing our checkIsAdult function.
Mocha - Mocha is a javascript testing framework running on Node.js and in the browser.
Chai - Chai is an assertion library for node and browser.
Let’s install those two packages
$ npm i mocha chai
Now, add Mocha as the testing framework in the package.json file. Add this line of code in the scripts
"scripts" : {
"test": "mocha"
}
When we run npm run test, Mocha looks for a folder named test and execute all the test files inside that folder.
Now, create a test file in the test folder. And import assert from chai, mock data, and our unit function
const chai = require('chai')const assert = chai.assert//importing the mock data for different scenariosconst {
UserWithAgeLessThan18,
UserWithAgeGreaterThan18,
UserWithAgeEqualTo18,} = require('./Mockdata')//importing the unit functionconst { checkIsAdult } = require('../main.js')
Mocha provides different utility functions to execute the test.
Example
describe - ‘describe’ can be used to group list of test related to a particular function(grouping test) it- ‘it’ is a test case
Let’s write our first test for our checkIsAdult function
describe('checkIsAdult should return true if age is greater than or equal to 18 and false if it is less than 18', function () {it('user with age greater than 18 return true', function () {assert.equal(checkIsAdult(UserWithAgeGreaterThan18().age), true)})it('user with age less than 18 return false', function () {assert.equal(checkIsAdult(UserWithAgeLessThan18().age), false)})it('user with age equal to 18 return true', function () {assert.equal(checkIsAdult(UserWithAgeEqualTo18().age), true)})})
Now, save the file and run
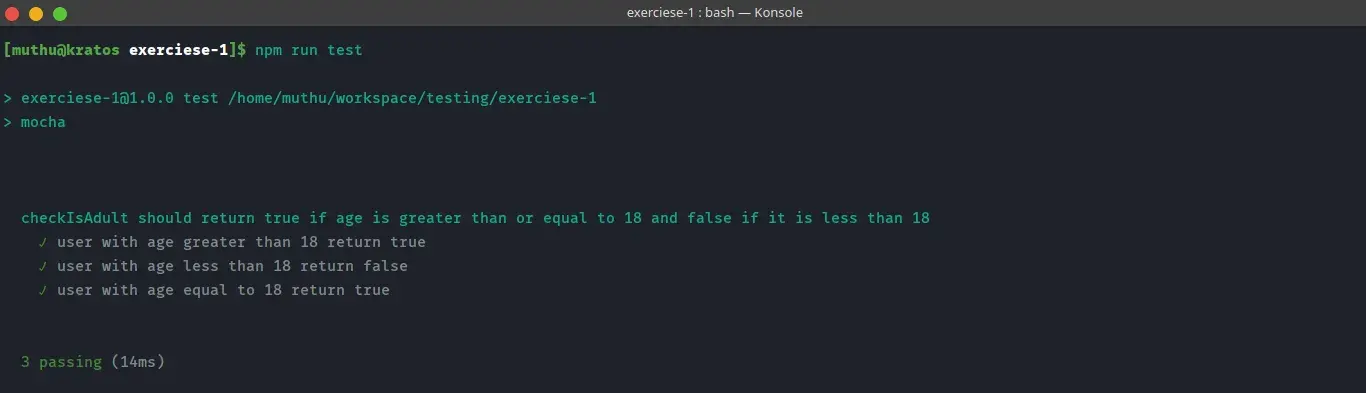
$ npm run test
All the test case passes.
The Output should be like this,
Need for splitting the business into separate functions
- If one function is dependent on another function like particular logics are nested inside, then in testing, we don’t know what throws the error. It creates confusion about what went wrong. That’s why we need to split the business logic into a separate function. Then we can test each function separately for a different set of values.
- We know the particular function of the function.
- Easy to debug.
- If there is an error, we know what function is causing the error.
For database query and API calls, we should create a separate function for that. So that if something went wrong we can check our code with the particular data and make sure that our business logic is working properly and the problem is with the API request or DB call.